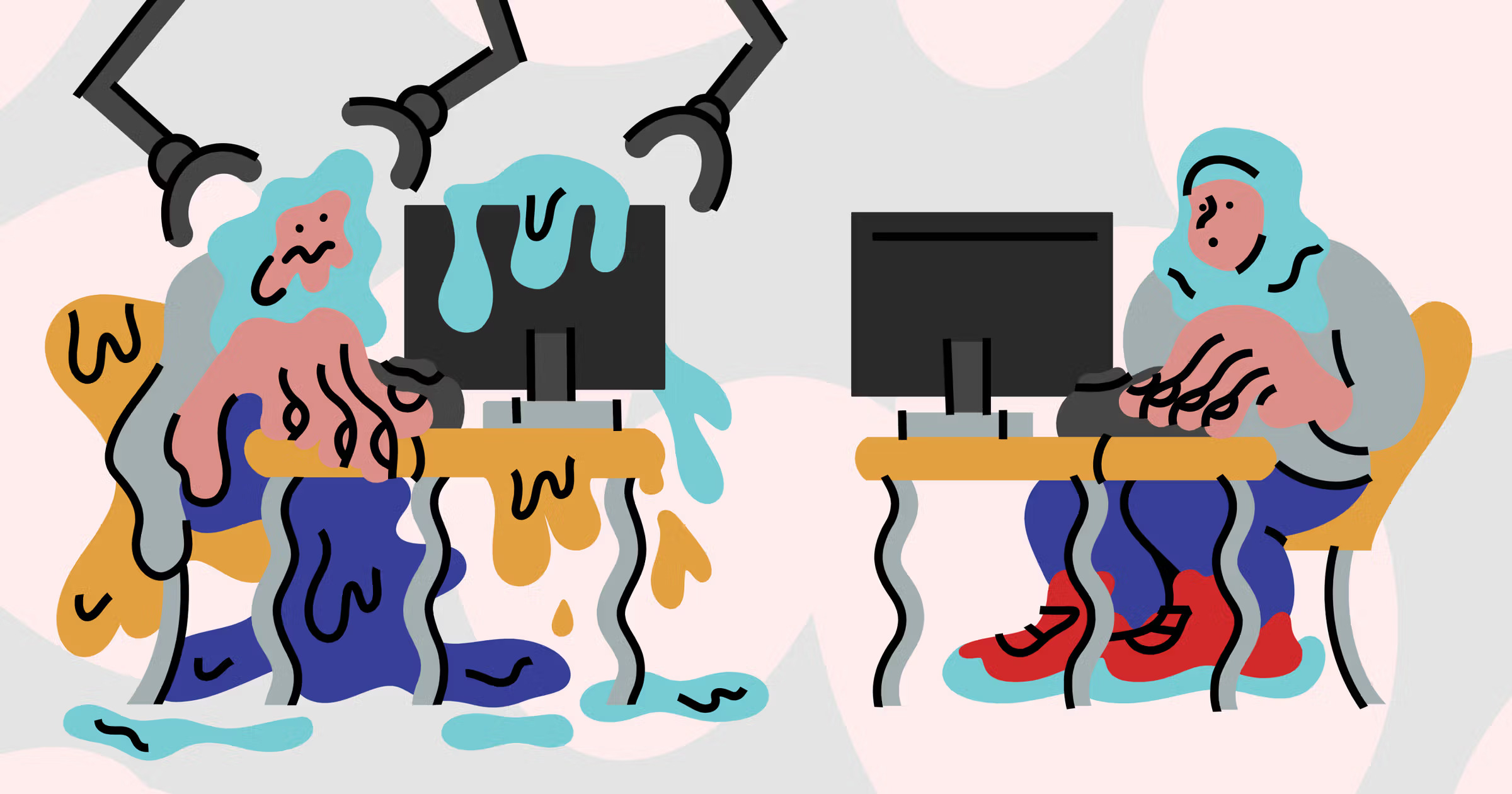
As we reflect on the significant shifts within the tech industry and prepare for the new year, it's crucial to revisit some of the most pressing debates shaping our field. Today, we delve into a topic that has sparked considerable discussion: the impact of generative AI on the role of junior engineers within tech companies.
A Personal Tech Journey My journey into the tech industry began at 19 when I moved to San Francisco to become a Unix sysadmin, quickly transitioning to a startup role focused on software engineering. Despite a non-traditional background and late exposure to computers, the low barriers to entry at the time facilitated my entry into tech. This open landscape is far cry from today’s high-entry thresholds, highlighting how the industry has matured from its "Wild West" days.
The Changing Tech Landscape Tech has evolved from a field with fluid roles and undefined standards to one with increasing requirements and formalities. This evolution mirrors the maturation seen in other fields, such as medicine or cinema, where standards and certifications have come to define professional entry points.
The Role of Apprenticeship in Software Engineering Software engineering remains fundamentally an apprenticeship industry. Despite the theoretical knowledge provided by degrees and bootcamps, the core skills of the trade are honed on the job. The path from novice to senior software engineer is a complex journey of continuous learning, often taking more than seven years of practical, on-the-ground experience.
Junior Engineers: The Backbone of Growth The tech industry's growth relies heavily on the continual infusion of junior engineers. They are not merely learners; they are vital contributors who bring fresh perspectives and adaptability to teams that might otherwise stagnate. The real challenge is not their initial productivity but rather the opportunity to grow and integrate within skilled teams.
Generative AI’s Capabilities and Limitations Recent discussions around generative AI have propelled the notion that such technologies could replace junior engineers by automating entry-level coding tasks. However, this perspective fails to grasp the full spectrum of engineering work. While AI can assist with code generation, the nuances of system integration, debugging, maintenance, and evolution require human oversight. AI tools, like Copilot or ChatGPT, should be seen as aids that streamline certain tasks, not as replacements for human engineers.
The Critical Need for Human Engineers Engineering teams thrive on diversity — in skill levels, experiences, and perspectives. Junior engineers play a critical role in maintaining this diversity, bringing new ideas and approaches that are essential for innovation. Moreover, the mentoring process itself is beneficial for both parties, helping to refine skills and solidify knowledge.
Investing in Junior Engineers Contrary to the view that hiring junior engineers is a cost, it’s an investment in the future. By nurturing juniors, companies cultivate a workforce capable of adapting to and shaping future technologies. The argument for integrating junior engineers into teams is not just ethical but strategic, fostering a dynamic and resilient engineering culture.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future with Junior Engineers As we move forward, the tech industry must recognize that generative AI is a tool, not a replacement for the human elements of creativity, problem-solving, and innovation that junior engineers bring. Building a successful engineering team means investing in people at all levels of their careers, understanding that today’s junior engineers are tomorrow’s leaders. It’s not just about filling positions but about fostering an environment where diverse talents can thrive and drive technological advancement forward.



Comments (0)